It has been said that 'what we don't know, won't hurt us,'
but this is not necessarily true. On the contrary, what we
don't know could kill us, especially when it comes to the
issue of radiation and its affects on the human body.
While radiation for the most part is invisible to the eye
and remains largely undetectable to the average person,
the body knows that it is there and responds to it. Thus,
being unaware of the presence of radiation does not
negate its reality nor its related health risks.Radiation: Review
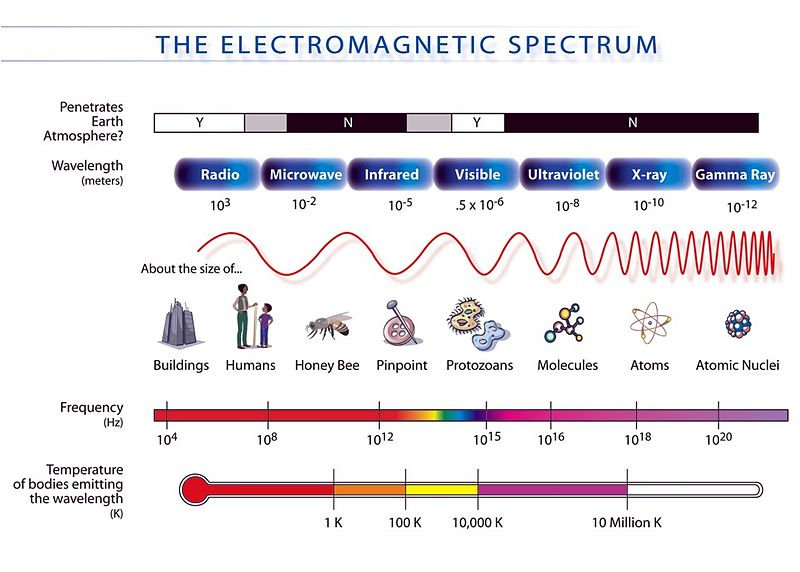
In Parts 1 and 2 of this series radiation was defined
as being a natural occurrence of energy moving
through space in waves that generate oscillating
electricity, frequencies, and magnetic fields. This
energy or radiation travels in various wavelengths,
each of which has its own respective range and
intensity as seen below.
Radiation comes from atoms that are in the process
of disintegrating and therefore are considered
'unstable' or radioactive. Unstable atoms have excess
internal energy as they move toward becoming stable.
These atoms are considered dangerous, because
their behavior is unpredictable and their unnatural,
'excited' charge is potentially harmful, especially to
the human body.Many forms of radiation have enough energy to break
chemical bonds in molecules or remove tightly bound
electrons from atoms, thus creating charged molecules
or atoms (ions). The ability of radiation to affect body
chemistry at the atomic level causes the production
of free radicals and pro-oxidants, i.e. mis-firing atoms
and molecules, in the body that act as scavangers to
'seek and destroy' healthy body cells. Free radical
and pro-oxidant proliferation is the underlying cause
the aging process as well as the destruction of the
body by sickness, pain, disease, and death.Radiation: Where is it?
If we can not see, smell, taste, or feel it, where is
radiation and how are we exposed to it? Two main
sources of radiation exist: natural and man-made,
and these two sources represent two types of
radiation: ionizing and non-ionizing. Ionizing radiation
is on the higher end of the electromagnetic scale:
gamma and x-rays plus alpha and beta particles.
Non-Ionizing radiation is located on the lower end
of the electromagnetic scale. Of these two types,
ionizing radiation poses the greater health risk,
because it is able to penetrate deeper into the body
and inflict harm to cells and living tissue.According to authorities, natural radiation accounts
for 82% of the average annual radiation dose for
humans and the remaining 18% is attributed to
man-made sources. This annual dosage is
detailed as follows:Internal- 11%- The human body is radioactive from
birth, possessing potassium-40, carbon-14, lead-210,
and other radioactive isotopes
Cosmic- 8%- charged particles from the sun and
celestial bodies that interact with the earth's atmosphere
to produce forms of radiation, predominately beta and
gamma rays
Terrestrial- 8%- 'Background radiation' that is found
naturally in soil, water, and vegetation. Low levels of
uranium and thorium are common, being ingested with
food and water. Other natural radioactive materials,
such as radon, are inhaled. Natural resources (air, water,
and soil) can become contaminated when they come
in contact with these naturally-occurring radionuclides.
Radon- 55%- Radon is a radioactive gas that you
cannot see, smell or taste, but it can be present in
homes, businesses, etc. It comes from the natural
decay of uranium that is found in nearly all rock and soils.
Radon usually moves from the ground up and migrates
into homes and other buildings through openings in any
ground in contact with the floor or a wall. Buildings trap
radon inside, where it accumulates and may become
a health hazard. Any home or building may have a radon
problem, including new and old homes, well-sealed
and drafty homes, and homes with or without basements.
Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in
the United States, with more than 20,000 Americans
dying each year from radon-related lung cancer. Only
smoking causes more lung cancer deaths and smokers
exposed to radon are at an even higher risk than
nonsmokers.
Medical X-rays- 11%- diagnostic x-rays, nuclear
medicine, and radiation therapy utilize major
radioactive isotopes such as Iodine-131, Cobalt-60,
Cesium- 137, Ts-99m, Ir-192, etc. The average
CTscan is equivalent to 442 chest x-rays.
Nuclear Medicine- 4%- Radiation therapy utilizes
x-ray, gamma rays, and radioactive iodine in
treating cancer.
Consumer Products- 3%- Tobacco: naturally-occurring
radioactive minerals accumulate on the sticky surfaces of
tobacco leaves as the plant grows.These minerals remain
on the leaves throughout the manufacturing process.
Additionally, the use of the phosphate fertilizer Apatite
which contains radium, lead-210, and polonium-210
also increases the amount of radiation in tobacco
plants.Man-made consumer products that contain
radiation:
- Ceramics- pre 1960 glazes for tiles, pottery,
and other ceramics often contain elevated
levels of naturally-occurring uranium, thorium,
and/or potassium-40, all of which emit alpha,
beta, and gamma rays. The popular FiestawareŽ
of the 1930s used uranium oxides to create a
distinctive orange-red glaze. Due to the high
incidence of foreign imports, no dinnerware
or household products are necessarily free
of radioactive materials.- Vaseline or canary glass contain small
amounts of uranium, which provide it's
yellow-green coloring and also makes it glow
under black lights- Clocks, watches, compasses, instrument
dials, emergency exit signs that glow in the
dark may contain radium, phosphor, tritium- Salt substitutes contain Potassium Chloride.
Approximately 0.01% of the Potassium found
in nature is Potassium-40, a radioactive isotope
with a half life of 1.28 billion years- Smoke detectors contain a small amount
(1 microcurie) of Americium-241, a radioactive
a radioactive element.- Thorium camping lantern mantles
- Antiques- furniture, clothing, jewelry, books,
dolls, dishes, and many other objects sold at
flea markets and antique shops likely contain
radioactive compounds. These items were
generally made and originally sold before
the health effects of radiation were well
understood and long before radiation
protection regulations were put in place.Radiation: Common sources
- Wireless technology
- Computers
- Portable cordless phones
- Cell phones
- Electronics in general
- Cell towers
- High Voltage Wires
- Transformers
- Substations
- Home wiring
- Household appliances
- TV
- Radio
- Pacemakers
- Digital Clocks
- Electric Clocks
- Fluorescent lights
- Microwave ovens
- Electric blankets
- Waterbeds
- Electric razors
- Hair Dryers
- Vacuum cleaners
- Can openers
- Neon lights
These sources largely represent what is known
as electro-pollution: EMF (Electro Magnetic Fields),
EMR (Electro Magnetic Radiation) and RF (Radio
Frequency). This pollution operates along the
electromagnetic spectrum with heaviest concentrations
near the source. While these forms of radiation diminish
with distance, they nevertheless remain active.Exposure to radiation can also result from
- Radioactive materials and waste- toxic,
heavy metal residues used in nuclear power
plants or manufacturing facilities.- Airport Scanners- utilize x-ray devices
- Radar detectors
- Smart meters
- Depleted Uranium (DU)- found in weaponry used
by the US military. Contains radioactive uranium.
'Depleted' is a mis-nomer as the uranium is yet
active.- White Phosphorus- found in military weaponry
that was introduced in the Gulf War.- Mail- letters, packages are exposed to radiation,
aka are irradiated, to protect the public from
harmful substances such as anthrax.- Food- most of the US food supply is irradiated,
i.e. exposed to high levels of radiation, Fruits
and vegetables receive over 100 RADs
(roentge absorbed does), while herbs and spices
receive over 3 Million RADS. Irradiation is a
government mandate for ensuring food safety
by destroying potential food pathogens while
increasing food shelf life. (Note: one RAD is the
normal radiation dose of an x-ray; irradiation
involves use of radioactive Cesium 137 and/or
Cobalt 60)Radiation: How much?
It is generally accepted that the average 'safe' dose
of radiation for humans is 360m/rem annually. However,
depending upon individual lifestyle, this dosage can
vary. These variables include occupation, living
location and conditions, diet, air travel, and personal
life habits. For example, frequent air travel increases
risk of radiation exposure as does smoking. Smokers
should figure an additional 1,300 mrem/yr to their
annual radiation dosage. This is due to radon decay
that is associated with tobacco products.Radiation: health risks
While no amount of radiation is healthy for
the human body, most medical, scientific, and
government authorities consider low level
exposure to be 'safe.' Nevertheless, depending
upon the individual, any amount of radiation
can have harmful affects, some of which
include:
- headaches
- fatigue
- dizziness
- skin rashes
- miscarriages
- low sperm count
- infertility
- heart problems
- neuro-endrocrine disruption
- leukemia
- cancer
- diabetes
- neurotransmitter imbalance
- compromised immune system
- stress
These symptoms are supported by the
following data relating radiation exposure levels
to health effects over designated time-frames:
Exposure
(rem)Health Effect Time to Onset
(without treatment)5-10changes in blood chemistry 50 nausea hours 55 fatigue 70 vomiting 75 hair loss 2-3 weeks 90 diarrhea 100 hemorrhage 400 possible death within 2 months 1,000 destruction of intestinal lining internal bleeding and death 1-2 weeks 2,000 damage to central nervous system loss of consciousness; minutes and death hours to days Numerous studies confirm that radiation exposure,
especially ionizing, mutates and/or destroys cells
and alters DNA. This fact is evidenced by the increasing
incidence of debilitating health problems that coincides
with the rise of modern technology. As much as modern
technology is remarkable, useful, and convenient, it has
proven to have a dark side. Some of these dark realities
include
- CTscans- one of the leading causes of
cancer in the US, causing over 15, 000
deaths every year and over 30,000 new
cases of cancer annually- There are 30,000- 50,000 new cases
of brain and eye cancer each year
worldwide that are attributed to cell
phone usage. Recent victim of cell
phone-related brain cancer was former
senator Ted Kennedy- In less than 5 minutes on a cell phone
radiation penetrates 1/2 way into the
brain of a toddler. (Note: brain cells do
not replicate, only die.)- Men who regularly carry their cell phones
near their groin are known to potentially
lower their sperm count by as much as
30%- Radio waves are believed to interfere
with heart pacemakers.- Military personnel exposed to Depleted
Uranium (DU) are radioactive and can pass
on this deadly form of radiation to those
around them: spouses, family, friends, etc.
DU is known to cause infertility, birth defects
neurological disorders, and more.- Excessive exposure to ionized radiation
can cause thyroid or other cancers.Radiation: How to avoid excessive exposure
Though we cannot escape the presence of radiation,
it is possible to protect ourselves from its harmful
affects. Therefore, for the sake of personal health,
safeguards should be considered. Some include:
- Limiting time spent near radiation sources
For example, limit and/or avoid use of cell
phones, computers, WiFi devices, etc.- Remain as far away as possible from
sources of radiation. The farther away from
a radiation source, the less is the exposure.
Sit back from computer monitors, place electric
devices, especially clocks, at least 4' away
from the bedside.- Avoid medical diagnostics and treatments,
i.e. CTscans, MRIs, X-rays, radiation therapy, etc.- Shield yourself from radiation sources.
The greater the thickness and density of shielding
around a radiation source, the lesser the exposure.- Deactivate or discard known radiation sources.
Disable exposure by removing batteries from cell
phones, unplugging computers, moving from
locations near transformers/substations/high
power lines. Discard microwave ovens. Discard
or discontinue use of products known to contain
radioactive materials.- Opt out of Smart meter technology
- Do not join the military, Coast/National Guard
or police.- Eat foods that are rich in anti-oxidants. While
all raw, living foods contain anti-oxidants, the
top ranking are berries (blueberries, strawberries,
blackberries, raspberries, cranberries), apples,
and beans (especially cacao).- Incorporate sea vegetables into your diet.
Trace minerals (especially iodine) in kelp, dulse,
bladderwrack, chlorella, and spirulina boost the
immune system, support thyroid health, and
naturally cleanse the body of harmful, heavy
metal residues associated with radioactive
particles.- Research product ingredients/materials,
especially food items, before purchasing.
Investigate country of origin. Avoid GMOs.- Invest in technology that neutralizes the
effects of radiation. Devices are available for
sale on the commercial market that effectively
harmonize electromagnetic radiation (EMR).
Applications protect cell phones, computers,
cars, whole house wiring, etc.In conclusion
Though radiation has always been with us, awareness
of its presence as well as its accompanying properties
has largely escaped us. Nevertheless, through education
and sometimes personal suffering, we learn what the
parameters of personal wellbeing include. Thus, if
we are to realize optimum health, we must consider
the unseen and address it as a present reality. How
we respond to radiation ultimately determines our
quality of life. Respecting radiation for what it is and
living within safe guidelines can spare us the dire
consequences of what is knowns as 'playing with fire.'
_________________________________________
References and further reading:
Natural Cures for Radiation- Dr. Cass Ingram
Radiation Measurement Explained
http://www.epa.gov/radtown/index.html
20-common-foods-most-antioxidants
http://www.blackcatsystems.com/science/radprod.html
Radiation Safety Devices
Please use PIN#407 when purchasing